Home » Nanoremediation: Using Nanomaterials and Nanotechnologies to Clean Up the Environment
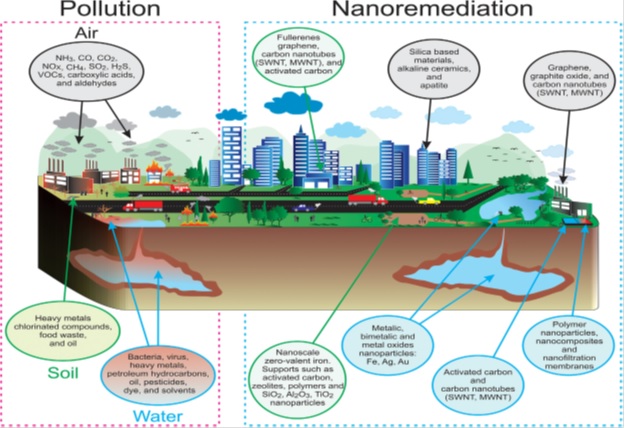
Several organic and inorganic pollutants that pose a risk to the environment and to human health have been brought about by various global events, such as industrial expansion and population growth. An developing science that has applications in many different sectors is nanotechnology.In instance, nanoremediation, which is defined as the use of designed materials to clean the environment, is a promising technique. It is a quick, effective, and efficient way to deal with persistent substances like pesticides, chlorinated solvents, halogenated chemicals, or heavy metals. Additionally, nanoremediation is a long-term solution to get rid of developing contaminants like pharmaceuticals or personal care items. Nanomaterials can be used in water, soil, or air media because to their diversity and adaptability.
Different types of nanomaterials are employed for Nanoremediation:
Due to the high hazards that contaminated groundwater poses to many ecosystems and the fact that clean water is essential for living things to support life, this issue worries environmental experts. Numerous ions, heavy metals, petroleum hydrocarbons, pesticides, radioactive elements, as well as new contaminants including pharmaceutics and personal care items, can contaminate water supplies. The main nanomaterials used in water remediation include carbon-derived materials, biopolymeric membranes, and metallic nanoparticles.
Due to their high reactivity, high surface-to-volume ratio, surface functionalization, and ability to alter physical parameters including size, shape, porosity, and chemical composition, nanomaterials have recently gained popularity for soil remediation. The combination of these attributes enables efficiency and selectivity in the capture of contaminants. Due to the in situ application, the intercalation of nanoparticles in the soil enables the cleaning of large areas while reducing costs and time. Nanoscale zero-valent iron, carbon nanotubes, and magnetic nanoparticles have dominated soil pollution Nanoremediation.
One of the biggest issues the world is dealing with in this century is air pollution since it has an influence on both public health and climate change. Particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), lead, and ground-level ozone, which is produced by chemical interactions between NOx and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), are the six most prevalent and dangerous outdoor air pollutants. The use of graphene oxides (GOs), graphite oxides, CNTs with highly reactive surface sites, and mesoporous silica materials with ordered and tunable porous structure, high surface area, large pore volume, and thermal stability have all been investigated as potential solutions to this issue.
Finding a balance between physical stability and sufficient surface activity that encourages contact with contaminants is thus a problem. The addition of functional groups to increase the removal of pollutants, such as -COOH and -NH2, may be able to prevent the agglomeration of nanoparticles under certain pH conditions through a concurrent mechanism of electrical charge repulsion, while stabilisation with non-ionic surfactants permits a decrease in flocculation. Non-ionic surfactants would not be required with this concept. The intricacy of the various mediums presents additional difficulty. With ligands from the polluted medium, the creation of a corona can obscure complex nanomaterials on the nanoparticle’s surface, favouring nanoremediation with earlier cleaning procedures.
Dr. Swapnila Roy
HOD, SOBAS
Lingaya’s Vidyapeeth
August 4, 2023RECENT POSTS
CATEGORIES
TAGS
Agriculture Agriculture future AI Architecture artificial intelligence BA English BA Psychology BTech Engineering Business management career Career-Specific Education career guide Career Opportunities career option career scope Civil engineering commerce and management Computer Science Computer science engineering Data science degree education Engineering engineering college Engineering students English Literature english program Exam tips Fashion Design Fashion design course Higher Education Journalism journalism and mass communication law Law career Machine Learning MA Psychology Master degree mathematics MBA Mechanical Engineering Pharmacy Psychology Research and Development students
University Address: Nachauli, Jasana Road, Faridabad, Haryana
Toll Free: 1800-120-4613
Mobile : 8447744303 | 8447744304 | 8447744306 | 8447744309
Address: C-72, Second Floor, Shivalik, Near Malviya Nagar,
Above HDFC Bank, New Delhi 110017
Ph.No. - 011-46570515 / 45138169 / 41755703 / +91-7303152412
Jagmani Kutir, Ground Floor, Road No-1, Rajeev Nagar,
Near Darbar Marriage Hall, Patna-800024, Bihar
Contact No: 9818352069/8130120095
Mail: [email protected]
Copyrights © 1998 - 2025 Lingaya's Vidyapeeth (Deemed To Be University). All rights reserved.
It is important to note that the following email IDs and domains are fraudulent and do not belong to our university.
LV only conducts physical/online verification of any document related to examination on the following email id: